Indianapolis, Indiana – Richard Bell, an Indiana copyright attorney, filed a lawsuit in the Southern District of Indiana alleging copyright infringement by numerous Defendants. The 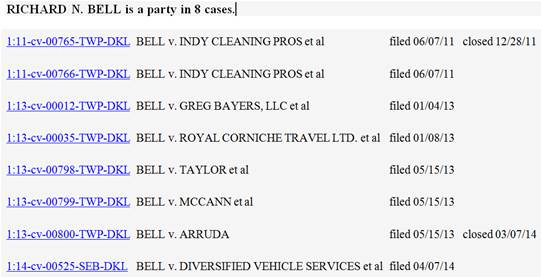 Defendants are: Diversified Vehicle Services of Marion County, Indiana; Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rhonda Williams of Indianapolis, Indiana; Forensic Solutions, Inc. of Waterford, New York; Heath Garrett of Nashville, Tennessee; CREstacom, Inc. of Fishers, Indiana; American Traveler Service Corp LLC, location unknown;
Defendants are: Diversified Vehicle Services of Marion County, Indiana; Cameron Taylor and Taylor Computer Solutions of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rhonda Williams of Indianapolis, Indiana; Forensic Solutions, Inc. of Waterford, New York; Heath Garrett of Nashville, Tennessee; CREstacom, Inc. of Fishers, Indiana; American Traveler Service Corp LLC, location unknown;
Mike Cowper of Martinsville, Indiana; Kimberly Hinds of Indianapolis, Indiana; Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute of Troy, New York; EasyStreet Realty of Indianapolis, Indiana; Drohan Management of Reston, Virginia; Metal Markets of Indianapolis, Indiana; Mattison Corporation of Indianapolis, Indiana; Industrial Heating Equipment Association of Taylor Mill, Kentucky; Junk Dawgs of Indianapolis, Indiana and WRTV of Indianapolis, Indiana. Mr. Bell is both the copyright lawyer and Plaintiff in this lawsuit.
Bell is a copyright attorney and a professional photographer. He contends that he is the owner of two copyrighted photographs of Indianapolis taken in March 2000. The photos have been registered with the U.S. Copyright Office.
Bell alleges that each Defendant, independent of each other Defendant, “created their individual website to promote and market their business” and placed the Plaintiff’s copyrighted photo on each of the Defendants’ respective websites. It is alleged that no Defendant had obtained the right to publish either photo but that each falsely represented otherwise to the world. Bell asserts that, as a result, Defendants have “realized and continue to realize profits and other benefits rightfully belonging to Plaintiff.” Each Defendant is accused of “willfully and deliberately” engaging in copyright infringement “with oppression, fraud, and malice.”
In his complaint, Bell lists the following claims:
• Count I: Copyright Infringement and Unfair Competition
• Count II: Theft
Bell asserts that he has already suffered, and is continuing to suffer, irreparable injury as a result of the alleged infringement of his copyrighted photos. Bell asks the court to declare that the Defendants’ conduct in using his photos violates his rights under Indiana law and the Copyright Act and asks the court to enjoin further infringing uses of his photos. Among other remedies, he seeks treble damages under Indiana statutory authority. He also asks for an accounting of all gains, profits and advantages derived by Defendants as a result of the alleged infringement and for the maximum allowable statutory and/or actual damages for each violation. Plaintiff also seeks reimbursement of costs and reasonable attorneys’ fees.
Practice Tip #1: The claims of this case appear calculated to trigger the “advertising injury” clause of many general business liability insurance policies. If a defendant has applicable business insurance, this may allow Mr. Bell to negotiate quicker settlements. Overhauser Law Offices, publisher of this Site, counsels clients on insurance coverage for insurance claims.
Practice Tip #2: This newest complaint initiates the latest of three ongoing cases filed by Mr. Bell asserting infringement of his photos. We have blogged about his copyright infringement litigation before. See here. The Indiana Lawyer also wrote today about Mr. Bell’s copyright infringement lawsuits. See here. The Indiana Business Journal ran a similar piece. Those articles include an interview with Paul Overhauser, Managing Partner of Overhauser Law Offices.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News


 Indianapolis, Indiana filed a lawsuit in the
Indianapolis, Indiana filed a lawsuit in the  “STRATOTONE” (the “Stratotone mark”),
“STRATOTONE” (the “Stratotone mark”),  Marion Superior Court to deny injunctive relief to
Marion Superior Court to deny injunctive relief to  geographic area restricted.
geographic area restricted. erroneous.
erroneous.  Indiana sued in Indiana state court alleging that
Indiana sued in Indiana state court alleging that  infringed the trademark Noble Roman’s, Registration No.
infringed the trademark Noble Roman’s, Registration No. 
 claims court (“trial court”) judgment in favor of Trilogy Health Services, LLC, d/b/a Springhurst Health Campus (“Springhurst”), on Springhurst’s claim against Hutchison and her now-deceased mother, Martha Farber (“Farber”), for payment of services provided to Farber while she was a resident at Springhurst. The Indiana Court of Appeals reversed.
claims court (“trial court”) judgment in favor of Trilogy Health Services, LLC, d/b/a Springhurst Health Campus (“Springhurst”), on Springhurst’s claim against Hutchison and her now-deceased mother, Martha Farber (“Farber”), for payment of services provided to Farber while she was a resident at Springhurst. The Indiana Court of Appeals reversed. trade secrets contained in documents submitted to the court were protected against public disclosure by both the Access to Public Records Act (
trade secrets contained in documents submitted to the court were protected against public disclosure by both the Access to Public Records Act ( Institute’s Project Management Professional (“PMP”) examination and certification process. PMA states that Burch was one of its most-trusted PMP course instructors in the Washington, D.C. area and that, in connection with that position, PMA provided him with access to its proprietary manner of conducting its PMP-examination preparation courses. Moreover, PMA claims that it commissioned Burch and Graywood, Burch’s company, to draft and prepare as a “work for hire” certain training modules that would be for PMA’s exclusive use.
Institute’s Project Management Professional (“PMP”) examination and certification process. PMA states that Burch was one of its most-trusted PMP course instructors in the Washington, D.C. area and that, in connection with that position, PMA provided him with access to its proprietary manner of conducting its PMP-examination preparation courses. Moreover, PMA claims that it commissioned Burch and Graywood, Burch’s company, to draft and prepare as a “work for hire” certain training modules that would be for PMA’s exclusive use.