New Albany, Indiana – Chief Judge Tanya Walton Pratt for the Southern District of Indiana dismissed a patent infringement suit filed by Plaintiff, Eddie M. Green, Jr. (“Green”) in March 2020 for lack of personal jurisdiction. 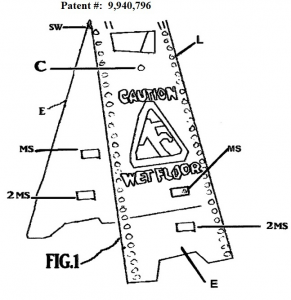
Green, who claimed Defendants, Ara Yavruyan and Chain Vault Inc., infringed on his U.S. Patent No. 9,940,796 for the “Yellow Fellow Safety Sign” filed his pro se Complaint in the Southern District of Indiana although he noted a California address for the Defendants. In response, Defendants filed a Motion to Dismiss arguing improper venue, lack of personal jurisdiction, failure to effect service, and that the Complaint fails to state a claim upon which relief can be granted.
In or around April 2020, the Court directed the Clerk to issue process, which was returned unexecuted by the United States Marshals Service (“USMS”) on July 9, 2020 as it could not locate the Defendants at the address listed on the Complaint. A second address was found and the Court ordered the USMS to issue process at the second address. On October 20, 2020, the USMS again returned an unexecuted summons, Complaint, and Order because it could not locate the second address for the Defendants. After being required to submit search evidence and a proper address to the Court, Green filed a Motion for Alias Summons which was granted on November 18, 2020. On November 19, 2020, having been served, the Defendants filed their Motion to Dismiss.
Over the course of one month after the filing of Defendants’ Motion to Dismiss, Green submitted a Motion for Summary Judgment, a Motion to Strike Declaration, and five filings opposing the Motion to Dismiss.
When a Court is faced with a Fed. Rule Civ. P. 12(b)(2) motion to dismiss for lack of personal jurisdiction, a plaintiff only needs to make a prima facie case of personal jurisdiction. However, “[i]f the defendant has submitted evidence in opposition to the implementation of jurisdiction, ‘the plaintiff must go beyond the pleadings and submit affirmative evidence supporting the exercise of jurisdiction.’” Additionally, the Court must employ a three-prong test to determine if there is specific jurisdiction: (1) the defendant purposefully directed its activities at residents of the forum, (2) the claim arises out of or relates to those activities, and (3) assertion of personal jurisdiction is reasonable and fair.”
Here, the Defendants claim neither reside or have any physical presence in Indiana or “continuous or systematic contacts with Indiana. Thus, the Court must use the three-prong test for specific jurisdiction. However, the Defendants claim they have no contacts with the state of Indiana at all and have therefore not availed themselves to specific jurisdiction. It does not appear Green was able to provide any evidence to the contrary and therefore, the Motion to Dismiss was granted.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News