Indianapolis, Indiana – Attorneys for Plaintiff, Secure Cam, LLC of Sheridan, Wyoming originally filed suit in the Northern District of California alleging that Defendant, Project Nursery, LLC of San Francisco, California infringed its rights in United States Patent No. 7,257,158, (“the ‘158 Patent”) for “System for Transmitting Video Images over a Computer Network to a Remote Receiver”. As of June 21,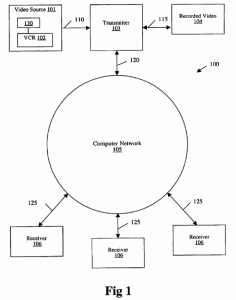 2018 this case has been transferred to the Southern District of Indiana. Plaintiff is seeking damages, costs, expenses, pre-judgment and post-judgment interest.
2018 this case has been transferred to the Southern District of Indiana. Plaintiff is seeking damages, costs, expenses, pre-judgment and post-judgment interest.
Plaintiffs allege that the Defendant’s face recognition readers and license plate recognition cameras that they manufacture, import into the United States, or offer for sale, and/or sell infringe at least Claim 12 of the ‘158 Patent. Other products alleged to infringe the ‘158 Patent include: Project Nursery 5” HD Dual Connect Wi-Fi Baby Monitor System, Project Nursery 4.3 Baby Monitor System with 2 Digital Zoom Cameras, Project Nursery Video Baby Monitor System with Digital Zoom Camera, Project Nursery 5” High Definition Baby Monitor System with 1.5” Mini Monitor, Project Nursery 4.3” Baby Monitor System with 1.5” Mini Monitor, and Project Nursery 4.3” Baby Monitor System. In the Complaint, plaintiffs point out seven separate elements included in the allegedly infringing products that are all elements in Claim 12 of the ‘158 Patent.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News