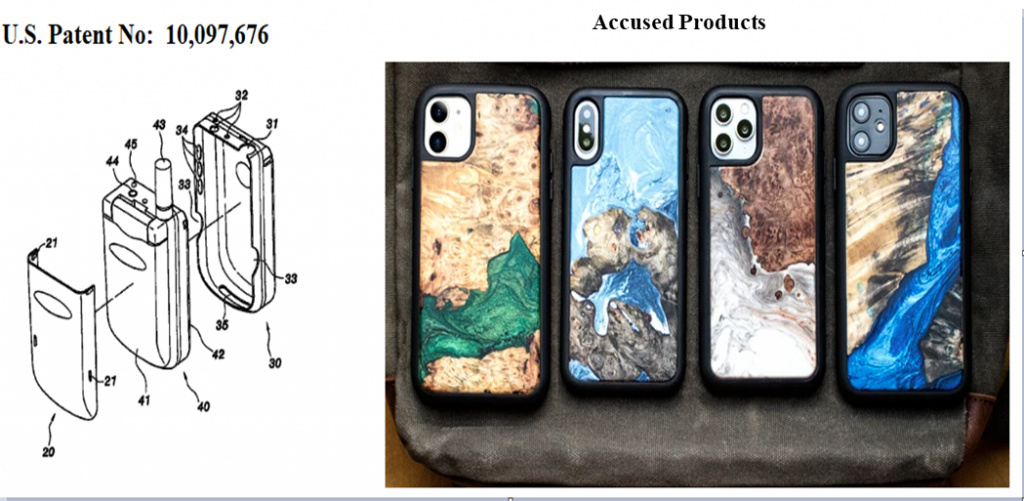
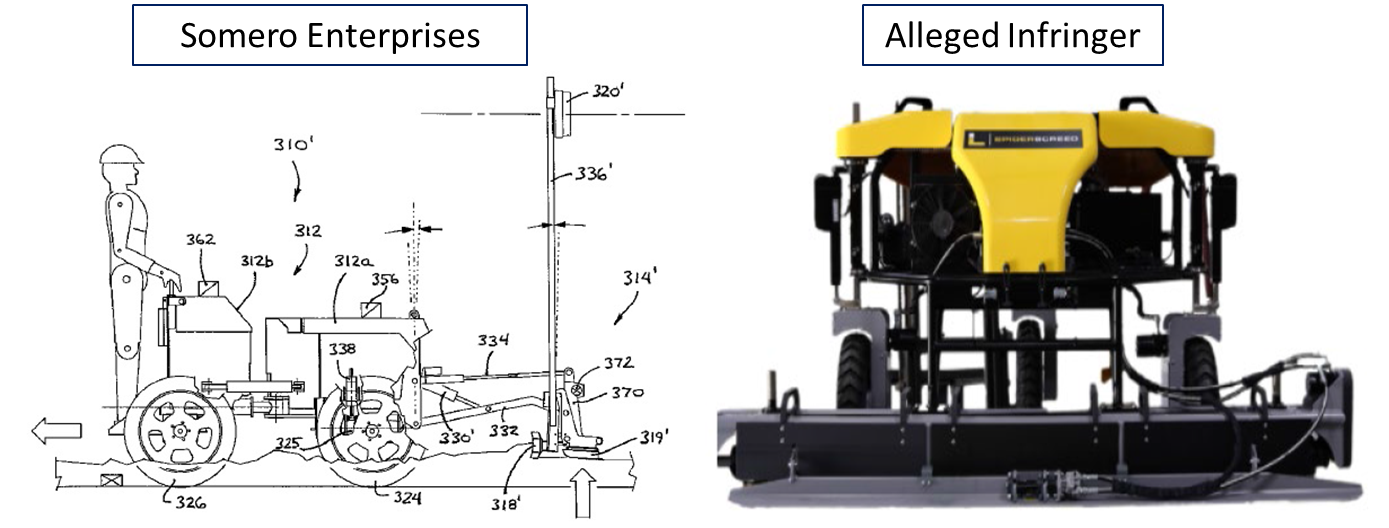
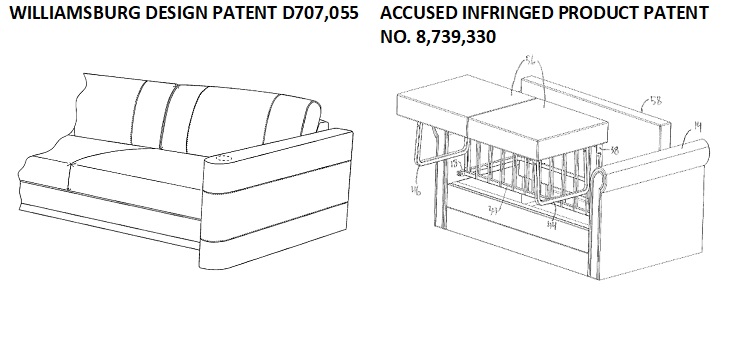
This suit is over the design of two bottle caps.
Plaintiff, Closure, claims it designed the bottle cap on the left, and Defendant, Novembal, got a patent on the bottle cap on the right. But Closure claims that it, not Novembal is the actual “inventor” of the bottle cap design. Perhaps fearing that Novembal was about to file suit, Closure in its home turf of New Jersey and trying to gain a home court advantage, took the initiative and sued Novembal in Indiana. Its Complaint sought to “correct the inventorship” of Novembal’s patent and to prevent Novembal from enforcing the patent against Closure. That suit is reported here: Closure Systems International Sues Novembal USA Seeking Correction of Inventorship. Not surpisingly, Novembal asserted a counterclaim for patent infringement.
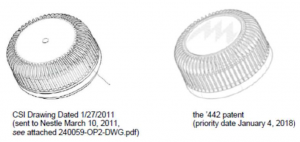 The twist is that in the infringement counterclaim, Novembal seeks a broad injunction. So broad, that it would prevent not just Closure, but some of Closure’s customers from infringing the patent. In its counterclaim, Novembal seeks:
The twist is that in the infringement counterclaim, Novembal seeks a broad injunction. So broad, that it would prevent not just Closure, but some of Closure’s customers from infringing the patent. In its counterclaim, Novembal seeks:
A permanent injunction enjoining CSI and its employees, agents, successors, partners, officers, directors, owners, shareholders, principals, subsidiaries, related companies, affiliates, distributors, dealers, and all persons in active concert or participation with any of them . . . from making, importing, promoting, offering, or exposing for sale, or selling the CSI Production Closures, or any other closures with designs confusingly similar to the claimed design of Novembal’s ‘442 patent.
One company that apparently gets its bottle caps from Closure is Nestle, one of the biggest sellers of bottled water. So far, no big deal. Except, Nestle is represented by the blue chip Washington DC patent law firm, Finnegan, Henderson, Farabow, Garrett & Dunner. Finnegan happens to be the same law firm that represents Novembal in the suit with Closure. So Finnegan is attempting to get an injunction for one client (Novembal) that would apply to another client, Nestle. Continue reading
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News