Indianapolis, Indiana – Indiana patent lawyers for Alcon Research, LTD of Fort Worth, Texas and Alcon Pharmaceuticals Ltd of Fribourg, Switzerland (collectively, “Alcon”) sued in the Southern District of Indiana alleging that Cipla Limited of Mumbai Central, Mumbai and Cipla USA Inc. of Miami, Florida (collectively, “Cipla”) infringed Olopatadine Formulations for Topical Administration, Patent Nos. 6,995,186 (the “‘186 patent”) and 7,402,609 (the “‘609 patent”), which have been issued by the U.S. Patent Office.
Texas and Alcon Pharmaceuticals Ltd of Fribourg, Switzerland (collectively, “Alcon”) sued in the Southern District of Indiana alleging that Cipla Limited of Mumbai Central, Mumbai and Cipla USA Inc. of Miami, Florida (collectively, “Cipla”) infringed Olopatadine Formulations for Topical Administration, Patent Nos. 6,995,186 (the “‘186 patent”) and 7,402,609 (the “‘609 patent”), which have been issued by the U.S. Patent Office.
According to the complaint, the Cipla entities are engaged in the generic-pharmaceutical business. Alcon asserts that one or more of the entities develops, manufactures, imports, markets, offers to sell and/or sells generic drugs throughout the United States.
Cipla filed an Abbreviated New Drug Application (“ANDA”) with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) seeking approval to manufacture and sell a generic version of Pataday™ ophthalmic solution, a drug product containing olopatadine hydrochloride. The two patents-in-suit, which Alcon claims to own, are asserted to cover Pataday™. Alcon contends that Cipla’s submission of this ANDA to obtain approval to engage in the commercial manufacture, use, offer for sale, sale and/or importation of Cipla’s ANDA product before the expiration of the patents-in-suit is an act of infringement under 35 U.S.C. § 271(e)(2)(A).
Alcon states that it believes that the Cipla entities are part of a vertically integrated and unified organization and that they will act in concert to introduce the generic version of Pataday™ to the United States market prior to the expiration of Alcon’s patents.
In the complaint, intellectual property attorneys for Alcon list the following claims:
• Count I: Infringement of the ‘186 Patent
• Count II: Infringement of the ‘609 Patent
• Count III: Declaratory Judgment of Infringement of the ‘186 Patent
• Count IV: Declaratory Judgment of Infringement of the ‘609 Patent
Alcon asks for a judgment that the ‘186 and ‘609 patents are valid and enforceable and have been infringed; a judgment providing that the effective date of any FDA approval of commercial manufacture, use or sale of Cipla’s ANDA product be not earlier than the latest of the expiration date of the patents-in-suit, inclusive of any extension(s) and additional periods of exclusivity; preliminary and permanent injunctions protecting products covered by the ‘186 patent prior to its expiration; preliminary and permanent injunctions protecting products covered by the ‘609 patent prior to its expiration; a judgment declaring that the commercial manufacture, use, sale, offer for sale or importation of Cipla’s ANDA product, or any other drug product covered by the ‘186 patent, will infringe, induce the infringement of, and contribute to the infringement by others of, that patent; a judgment declaring that the commercial manufacture, use, sale, offer for sale or importation of Cipla’s ANDA product, or any other drug product covered by the ‘609 patent, will infringe, induce the infringement of, and contribute to the infringement by others of, that patent; a declaration that this is an exceptional case and an award of attorneys’ fees; and costs and expenses.
Practice Tip:
India is the world’s leading exporter of generic drugs. Some Indian manufacturers are aggressively seeking to have their generic versions approved by the FDA well before a brand-name drug’s patent(s) expire. This has led to a substantial amount of patent litigation against Indian companies, as the difference in market price between brand-name drugs and their generic counterparts can be enormous.
In addition to Indian companies being subject to litigation in the United States, Indian courts are also actively engaged in the ongoing dispute over intellectual property rights. Those courts, as well as the Indian government, have in several notable instances found in favor of Indian generic-drug manufacturers and against intellectual property holders in the United States. For example, in 2012, a decision by India’s Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks granted a “compulsory license” of the patented cancer drug Nexavar.
According to this decision, Bayer must license Nexavar to Natco Pharma, an Indian company, in exchange for a 6% royalty on Natco’s net sales. The generic drug will be sold in India for $176 per month instead of the $5,600 per month that Bayer had been charging in that market.
While a provision exists within the World Trade Organization‘s Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (“TRIPS”) Agreement that allows for compulsory licensing of pharmaceuticals, it has been used only infrequently, usually for drugs that treat AIDS. This was the first time such compulsory licensing was granted in India. India is only the second country, after Thailand, to grant a compulsory license to a cancer drug.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News


 Indiana (“Lilly”) filed a lawsuit in the
Indiana (“Lilly”) filed a lawsuit in the 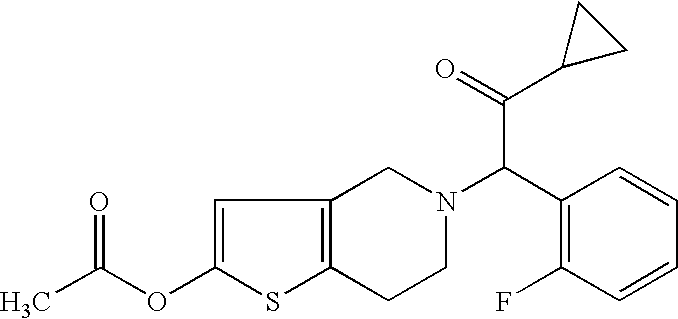 This is a civil action for patent infringement. It arises out of the filing by Defendant Par of an Abbreviated New Drug Application (“ANDA”) with the
This is a civil action for patent infringement. It arises out of the filing by Defendant Par of an Abbreviated New Drug Application (“ANDA”) with the 
 including mesothelioma. However, certain side effects were troublesome, including treatment-related hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity.
including mesothelioma. However, certain side effects were troublesome, including treatment-related hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity. 


