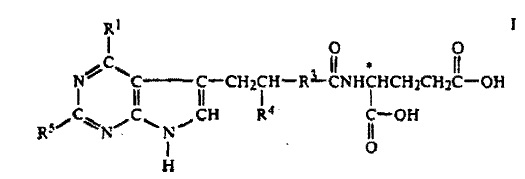
Indianapolis, IN – A patent infringement judgment from the Southern District of Indiana will be reviewed by the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals. In May, Chief Judge Richard L. Young of the Southern District of Indiana issued a verdict and judgment in favor of plaintiffs Alcon Research Ltd., Alcon Laboratories, Inc., both of Fort Worth, Texas and Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd. (f/k/a Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd.) of Tokyo, Japan, after a bench trial on the plaintiff’s patent infringement claims against Apotex, Inc., of Ontario, Canada and Apotex Corp. Weston, Florida. Alcon filed a complaint alleging Apotex infringed patent no.5,641,805, TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC FORMULATIONS FOR TREATING ALLERGIC EYE DISEASES, which has been issued by the US Patent Office.
Chief Judge Young presided over a bench trial April 26, 2010 to May 7, 2010, and final arguments were presented to the court on August 3, 2010. The Court found that plaintiffs had “proven, by a preponderance of the evidence, that the Defendants’ generic equivalent of Plaintiffs’ patented allergy topical ocular medication,  Patanol®;, infringed claims 1-8 of the ‘805 patent[,]” and that the defendant failed to show, by preponderance of evidence, that the patent claims were invalid. The court also found that the defendants failed to prove, by preponderance of evidence, that the ‘805 patent is unenforceable due to inequitable conduct.
Patanol®;, infringed claims 1-8 of the ‘805 patent[,]” and that the defendant failed to show, by preponderance of evidence, that the patent claims were invalid. The court also found that the defendants failed to prove, by preponderance of evidence, that the ‘805 patent is unenforceable due to inequitable conduct.
Apotex has appealed the case to the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals (docket number 2011-1455). Apotex’s brief was filed on October 3, 2011, and Alcon’s brief is due on December 23, 2011.
Practice Tip: One of the defenses raised by Apotex was to claim the patent was unenforceable due to inequitable conduct. Apotex claimed that one of the inventors of the ‘805 failed to disclose results of certain tests and other data in the patent application. Apotex claimed the inventor as well as the attorney who filed the patent application violated their duty of candor to the PTO, which is imposes pursuant federal regulations 37 C.F.R. § 1.56(c). Alcon, however, presented evidence that the tests in question were believed to be inconclusive and that the inventor simply forgot about another test. Under the totality of circumstances, the court found that a finding of deceptive intent was not warranted. The court, therefore, declined to find that the patent should not be enforceable under the theory of inequitable conduct.
In addition, the court held that Apotex could not raise an additional theory of invalidity – invalidity for lack of a written description – until after the trial. The court found that the late disclosure had prejudiced the plaintiff and therefore refused to consider the new theory.
Continue reading
 suit in the Southern District of Indiana alleging that Accord Healthcare, Inc., USA of Durham, North Carolina infringed patent no. 7,772,209, Antifolate combination therapies, which has been issued by the US Patent Office.
suit in the Southern District of Indiana alleging that Accord Healthcare, Inc., USA of Durham, North Carolina infringed patent no. 7,772,209, Antifolate combination therapies, which has been issued by the US Patent Office. Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News