Indianapolis, Indiana – National Collegiate Athletic Association (“NCAA”) of Indianapolis, Indiana sued in the Southern District of Indiana alleging trademark infringement and unfair competition.
Indianapolis, Indiana – National Collegiate Athletic Association (“NCAA”) of Indianapolis, Indiana sued in the Southern District of Indiana alleging trademark infringement and unfair competition.
NCAA’s trademarks, which have been registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark office (“USPTO”), pertain to the following uses of FINAL FOUR and MARCH MADNESS:
| MARK | GOODS/SERVICES | REG NO. & DATE |
| FINAL FOUR | Association services, namely, conducting annual basketball tournaments at the college level | 1,488,836;
May 17, 1988 |
| FINAL FOUR | Promoting the goods and services of others by allowing sponsors to affiliate their goods and services with collegiate championship tournaments | 2,377,720;
Aug. 15, 2000 |
| FINAL FOUR | Printed matter, namely, guides in the field of sports; Luggage, namely, portfolios, backpacks, duffle bags, rolling luggage, garment bags, briefcases, athletic bags and tote bags; and Entertainment services, Namely, providing information in the field of college sports via the Internet | 2,964,266;
June 28, 2006 |
| MARCH MADNESS | Entertainment services, namely, presentation of athletic and entertainment personalities in a panel forum | 1,571,340;
Dec. 12, 1989 |
| MARCH MADNESS | Entertainment in the nature of basketball tournaments between college teams | 2,485,443;
Sept. 4, 2001 |
| MARCH MADNESS | Telecommunications services; namely the transmission of voice, data, images, audio, video and information via local and long distance telephone, satellite and global computer networks; leasing telecommunications equipment, components, systems and supplies; electronic mail services; telephone voice messaging services; providing multiple-user access to global computer networks to transmit, receive and otherwise access and use information of general interest to consumers; web casting of athletic games, tournaments, exhibitions, and events via the Internet | 3,025,527;
Dec. 13, 2005 |
Defendants in this Indiana trademark lawsuit are Kizzang LLC of Las Vegas, Nevada and Robert Alexander, the founder and owner of the business. They are in the business of providing nationwide Internet-based promotions that award prizes for predicting the results of sporting events. Plaintiff states that they have branded their NCAA-related services using the mark FINAL 3.
Plaintiff further asserts that Defendants had planned to adopt APRIL MADNESS for the same services as FINAL 3, but that they delayed doing so upon learning that NCAA objected to their use of FINAL 3. Kizzang has applied for federal trademark registrations for both marks with the USPTO.
Indiana trademark attorneys for Plaintiff contend that Defendants adopted both names because of their similarity to the marks used by NCAA and that Defendants did so with the intention of exploiting the goodwill associated with FINAL FOUR and MARCH MADNESS. In this lawsuit, filed in federal court, the following claims are made:
- Trademark Infringement Under 15 U.S.C. § 1114
- Trademark Infringement Under 15 U.S.C. § 1125(a)
- Trademark Dilution Under 15 U.S.C. § 1125
- Common Law Unfair Competition
Plaintiff asks for various remedies from the court, including a judgment of willful and intentional violations of 15 U.S.C. §§ 1114, 1125 and Indiana common law; injunctive relief including restraining Defendants from further use of FINAL 3 and APRIL MADNESS as well as an order that the USPTO deny registration for the marks; damages, including treble damages; and attorneys’ fees.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News







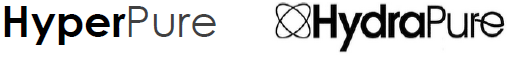 Plaintiff further contends that Defendant Legend chose the HYPERPURE mark in bad faith in an attempt to associate Defendant’s products with Plaintiff’s trademark and, in so doing, appropriate the goodwill that Plaintiff has built in the brand.
Plaintiff further contends that Defendant Legend chose the HYPERPURE mark in bad faith in an attempt to associate Defendant’s products with Plaintiff’s trademark and, in so doing, appropriate the goodwill that Plaintiff has built in the brand.