How should I protect my intellectual property?
Different types of intellectual property are protected by different means.
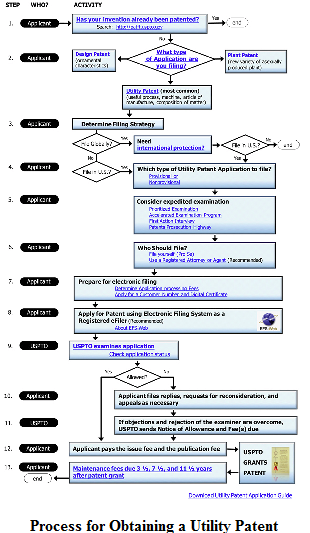
In the United States, patents may be available to any person who “invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof.” Patent protection must be sought by application with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”). There are three types of patents:
• Utility patents may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof;
• Design patents may be granted to anyone who invents a new, original, and ornamental design for an article of manufacture; and
• Plant patents may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers and asexually reproduces any distinct and new variety of plant.
More information on patents is available here: USPTO’s patent process website.
Trademarks protect words, names, symbols, sounds, or colors that distinguish goods and services from those manufactured or sold by others and to indicate the source of the goods. Registration with the USPTO is not required, but does provide certain advantages. More information on trademarks is available here:
Online IPR Tutorial (Module 3)
USPTO’s trademark process website
Copyrights protect original works of authorship, including literary, dramatic, musical, artistic and certain other works, both published and unpublished. In the United States, the U.S. Copyright Office handles copyright registration that, although not required for protection, does confer advantages. More information on copyrights is available here:
Online IPR Tutorial (Module 3)
U.S. Copyright Office website
How long does patent, trademark or copyright protection last?
A U.S. utility patent is generally granted for 20 years from the date the patent application is filed; however, periodic fees are required to maintain the enforceability of the patent.
A design patent is generally granted protection for 14 years measured from the date the design patent is granted.
A U.S. trademark generally lasts as long as the trademark is used in commerce and defended against infringement.
Copyright protection is for a limited term. For works created after January 1, 1978, copyrights last for 70 years after the death of the author. For works “made for hire” (covering the usual type of work owned by a small business), the copyright lasts for a term of 95 years from the year of its first publication or a term of 120 years from the year of its creation, whichever expires first. For more detailed explanation of copyright terms, visit the Copyright Office webpage or consult this guide on Duration of Copyright provided by the Copyright Office.
A trade secret can be protected indefinitely as long as the secret is commercially valuable, its value derives from the fact that it is secret, and the owner take reasonable precautions to maintain its secrecy.
The information presented on this site does not constitute legal advice. It should not be considered to replace advice from an Indiana intellectual property attorney. An Indiana intellectual property lawyer can help you with matters involving patents, trademarks, copyright or trade secrets.
 Indiana Intellectual Property Law News
Indiana Intellectual Property Law News

