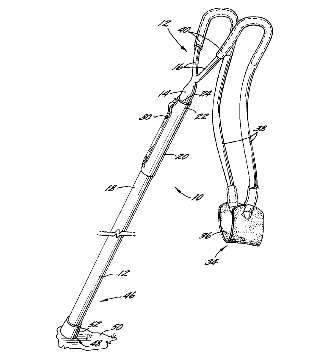
Indianapolis, Indiana – An Indiana patent attorney for Sherrill, Inc. of Greensboro, North Carolina (“Sherrill”) filed a patent infringement complaint in the Southern District of Indiana alleging that TreeStuff, Inc. of Indianapolis, Indiana infringed Patent No. 5,887,577 entitled “Apparatus for Propelling a Projectile,” which has been registered by the U.S. Patent Office.
Plaintiff Sherrill asserts ownership by assignment to United States Patent No. 5,887,577 (“the ‘577 Patent”), which was issued to William T. Sherrill in 1999. It claims that TreeStuff manufactures, uses, offers for sale, and/or sells a product that infringes upon that patent, namely TreeStuff’s Stein Tekichu Throw Weight Launcher.
In November 2014, Sherrill sent a cease-and-desist letter to TreeStuff. In that letter, it identified the ‘577 Patent, stated that the Stein Tekichu Throw Weight Launcher infringed upon certain claims of the ‘577 Patent and demanded that TreeStuff cease all infringing activities.
Sherrill claims that TreeStuff did not respond to this letter but instead continued to use, offer to sell, and/or sell the accused product. Sherrill contends that, by engaging in these activities, TreeStuff has directly infringed, and will continue to directly infringe, at least claim 8 of the ‘577 Patent under 35 U.S.C. § 271(a) literally and/or under the doctrine of equivalents. Sherrill also suggests in its complaint that it is “reasonable to infer” that TreeStuff also intended to induce infringement. TreeStuff has also been accused of contributory infringement. Sherrill asserts that TreeStuff’s infringement has been and continues to be willful and deliberate.
In its complaint, filed by an Indiana patent attorney, Sherrill asks that the court:
• Declare that the ‘577 Patent was duly and legally issued, is valid and is enforceable;
• Enter judgment that defendant TreeStuff has infringed at least claim 8 of the ‘577 Patent;
• Enter judgment that defendant TreeStuff has induced infringement of at least claim 8 of the ‘577 Patent;
• Enter judgment that defendant TreeStuff has contributed to infringement of at least claim 8 of the ‘577 Patent;
• Enter a preliminary and permanent injunction enjoining defendant TreeStuff and its agents from any further sales or use of their infringing products and any other infringement of claims of the ‘577 Patent, whether direct or indirect, pursuant to 35 U.S.C. § 283;
• Award damages to compensate Sherrill for defendant TreeStuff’s infringement of the claims of the ‘577 Patent pursuant to 35 U.S.C. § 284;
• Award enhanced damages pursuant to 35 U.S.C. § 284;
• Award pre-judgment and post-judgment interest and costs to plaintiff Sherrill in accordance with 35 U.S.C. § 284; and
• Deem the case to be “exceptional” within the meaning of 35 U.S.C. § 285, entitling plaintiff Sherrill to an award of its reasonable attorney fees, expenses and costs in this action.










 Delaware – A third member of an international computer hacking ring has pleaded guilty to conspiring to break into computer networks of prominent technology companies to steal more than $100 million in intellectual property and other proprietary data.
Delaware – A third member of an international computer hacking ring has pleaded guilty to conspiring to break into computer networks of prominent technology companies to steal more than $100 million in intellectual property and other proprietary data.